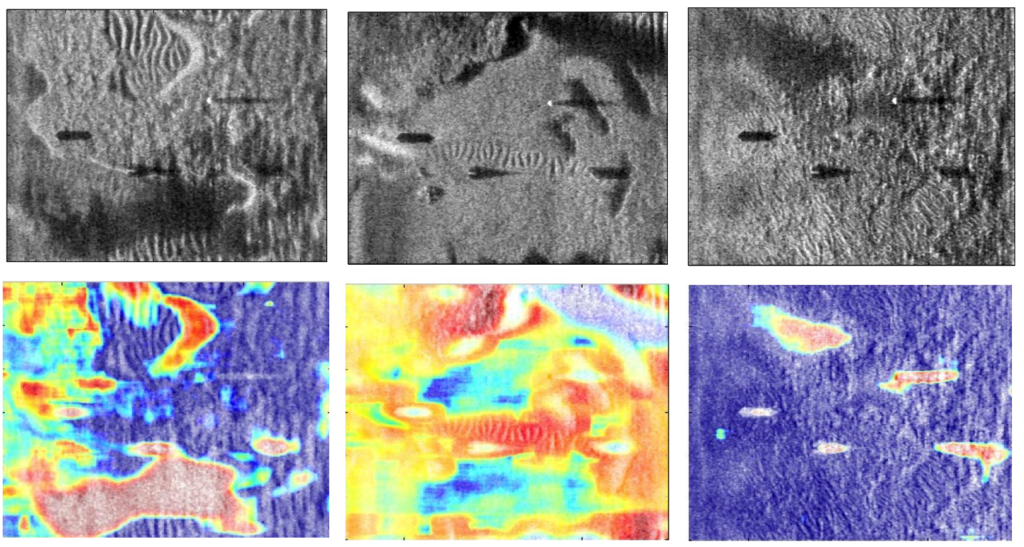
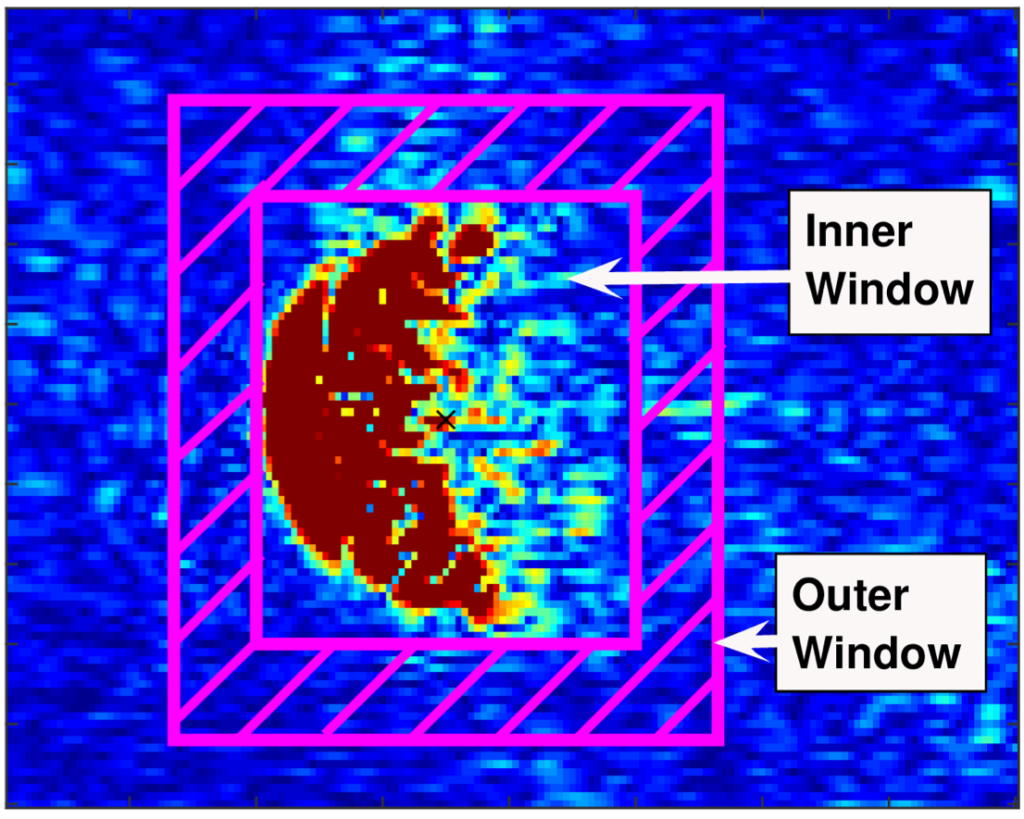
Synthetic Aperture Sonar (SAS) imaging systems produce high-resolution seabed imagery useful for underwater target detection and scene understanding. One of the challenges for underwater context identification is that the boundaries between seabed contexts (e.g., sand ripple, sea grass, hard-packed sand) are usually gradual with wide regions of transition. We developed a Multiple Instance Learning (MIL) based approach that can produce possibilistic seabed context identification maps.
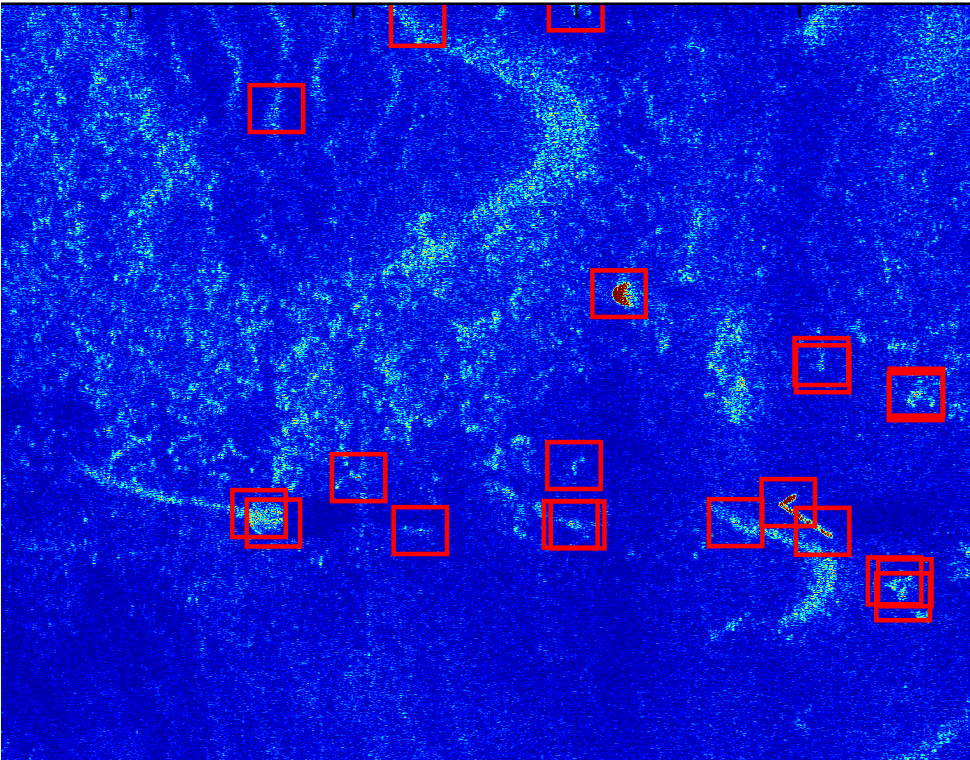
In addition, the characteristics of target objects in SAS imagery vary across different seabed contexts. We developed an end-to-end environmentally-adaptive target recognition system for SAS imagery that performs target recognition while accounting for environmental contexts.
Associated Publications
- Environmentally-Adaptive Target Recognition for SAS Imagery, SPIE DCS Conference, 2017.
- Multiple-instance Learning-based Sonar Image Classification, SPIE DCS Conference, 2017.
- Possibilistic context identification for SAS imagery, SPIE DCS Conference, 2015.